Disease-information
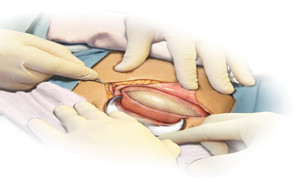
Cesareans
delivery is the most common risk factor for postpartum maternal infections,
which occurs at a rate of 18%–38%. Factors that have been associated with an
increased risk of infection among women who have a cesarean delivery include
emergency cesarean section, labor and its duration, ruptured membranes and the
duration of rupture, t...
Community-acquired pneumonia (CAP)
is a significant cause of respiratory morbidity and mortality in children,
especially in developing countries. Worldwide, CAP is the leading cause of
death in children younger than five years.
Clinical assessment requires
careful evaluation of clinical features, severity, and evidence of
complications....
The British Medical Journal (BMJ):
British Society of
Gastroenterology (BSG) and British Society of Paediatric Gastroenterology,
Hepatology and Nutrition (BSPGHAN) joint consensus guidelineThese joint consensus guidelines
from the British adult and paediatric gastroenterology societies utilize the
GRADE methodology to make recommendatio...
The British Medical Journal (BMJ):
British Society of Gastroenterology (BSG) and British
Society of Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition (BSPGHAN)
joint consensus guidelines
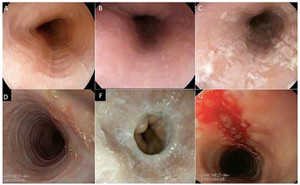
Eosinophilic oesophagitis is a condition characterised by
symptoms of dysphagia and/or food impaction in adults, and feeding problems,
abdominal...
The British Pharmacological Society Journal: Published: 05 September 2019
Penicillin’s are widely used during
pregnancy for various bacterial infectious indications. Amoxicillin, rapidly
crosses the placenta following absorption to the bloodstream, It is prescribed
both as a sole medicine as well as in combination with clavulanic acid mos...
Urinary
tract infections (UTIs) represent a common pathology among female patients,
leading to overprescribing antibiotics, globally. The emergence of the COVID-19
pandemic has dramatically increased the incidence of this particular viral
pneumonia with secondary bacterial superinfection, resulting in continuous
therapeutic or prophylactic...
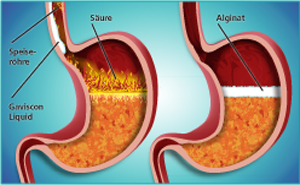
Heartburn is a cardinal symptom of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease
(GERD) and is among the most common patient complaints encountered by physicians.
TAKE HOME MESSAGE:
This study compared the effect of Antacid & Alginate Liquid to an antacid
in controlling post-prandial acid reflux in GERD patients.
The current investigation demons...
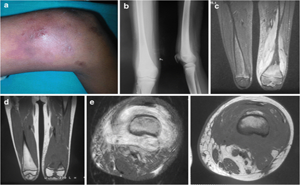
PubMed Central: Published on 2020 August
AHOM was defined as any bone
infection with a period between symptoms onset and diagnosis < two weeks.
AHOM was defined complicated in the
presence of sepsis, septic shock, arthritis, cellulitis, sub-periosteal or
muscle abscess, deep vein thrombosis pathological fracture, septic emboli or
hosp...
The British Medical Journal (BMJ): Published 17 May 2022
Compared with vaginal delivery,
caesarean section carries a substantially increased risk of maternal postpartum
infections. This risk can be reduced by routine provision of prophylactic
antibiotics.
Evidence from randomized controlled
trials shows that antibiotics are more effe...
Expert
Opinion on Drug Metabolism & Toxicology Journal: Published on: 11 Jul 2022
Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) are
widely prescribed for the treatment of gastric acid-related disorders and the
eradication of Helicobacter pylori. In addition, they are routinely prescribed
for the prevention of gastrointestinal bleeding in patients receiv...
Hypertension is considered a major
health problem around the world. It’s associated with increasing risk of
mortality due to its complication which has a great impact on patient’s life
quality.
Chronic uncontrolled hypertension
is a significant risk factor for cardiovascular mortality and morbidity,
strokes, heart failure, and renal fai...
Journal of Minimally Invasive
Gynecology: Published on December 2020
Endometriosis is a common condition
affecting women of reproductive age, often presenting with pelvic pain and
infertility. In addition to significantly impacting a woman’s quality of life,
the treatment of endometriosis carries a considerable economic burden.
TAKE...